#women revolution
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
saying F U to the regime again and again: a quick update on women vs IR regime
Famous Iranian actresses have been appearing in public without a mandatory hijab. This has been happening since the beginning of the protests. Last month, Kiumars Pourahmad, a well known Iranian screenwriter and director, committed suicide. He had a history of criticizing the regime's political decisions. At his funeral, some of the famous actresses attended without mandatory hijab.

You can see Fateme Motamedarya, Katayoun Riyahi, and Golab Adineh in these pictures from the funeral. Ms. Riyahi was one of the first celebrities who took her hijab off at the start of the Jina (Mahsa) Amini protest and for that she's been the target of IRGC harassment and has been to court.
Last week, in the ceremony of screening of the final episode of Lion's Skin (a persian crime show), actress Pantea Bahram participated without hijab. The manager of Tehran’s Lotus Cinema, where the ceremony was held, was fired for letting her attend without hijab.
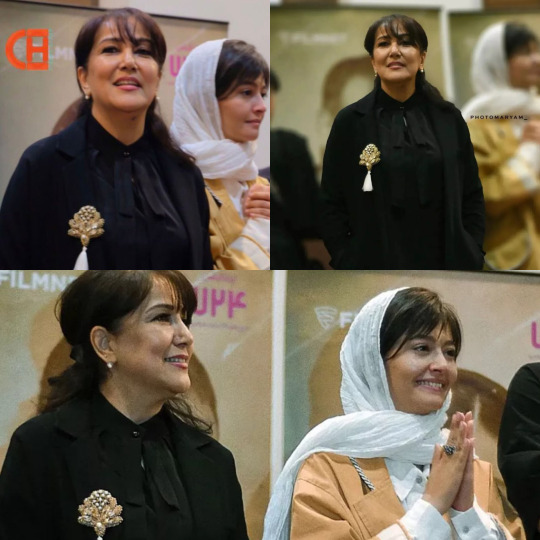

Other than prosecution, the regime has blocked these celebrities' bank accounts. Basij and IRGC members have also attacked and harassed these women online and in real life.
Students on university campuses take off their hijabs. There's an installed version of morality police in universities that monitor students' styles. Female students must wear "appropriate" hijab and male students must wear "manly" clothes (one of my guy friends once was asked to go back home and change his shoes because they were red casual loafers. Apparently that's gay!). When you enroll in Iranian universities, the first thing you do is to go to the security office and sign an agreement that says you promise to follow the Islamic dress code. There are posters all over the campus that says things like "hijab is security" "respect the islamic hijab" and "not wearing appropriate hijab (tight short clothes, too much hair, makeup, etc) would result in legal action". So not wearing hijab on campus, where a lot of security cameras are installed and it's easy to identify you, is a big deal.
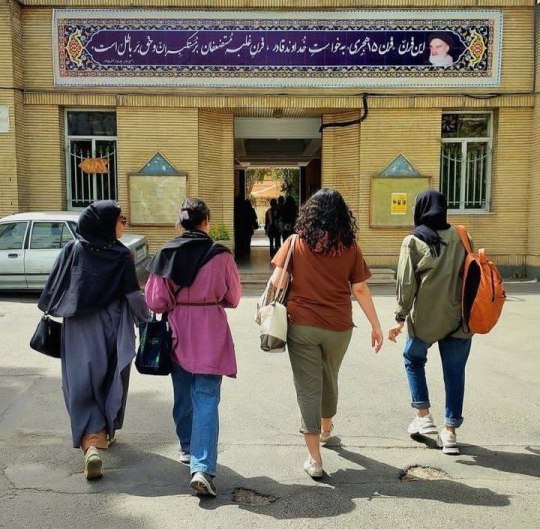
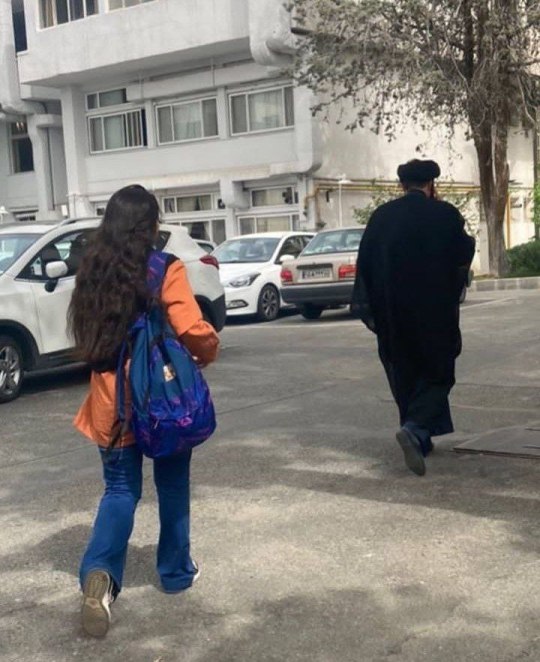
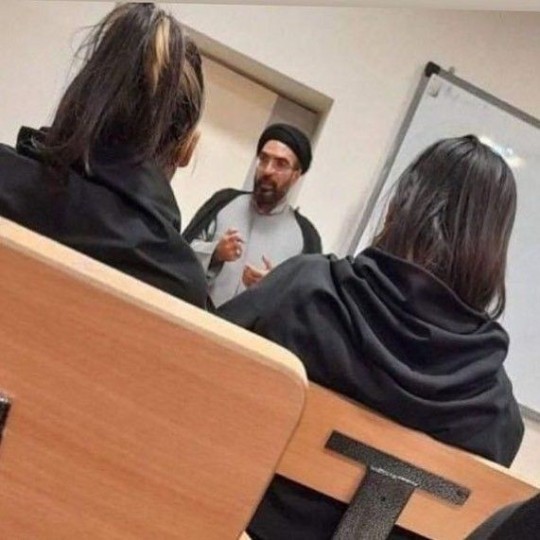
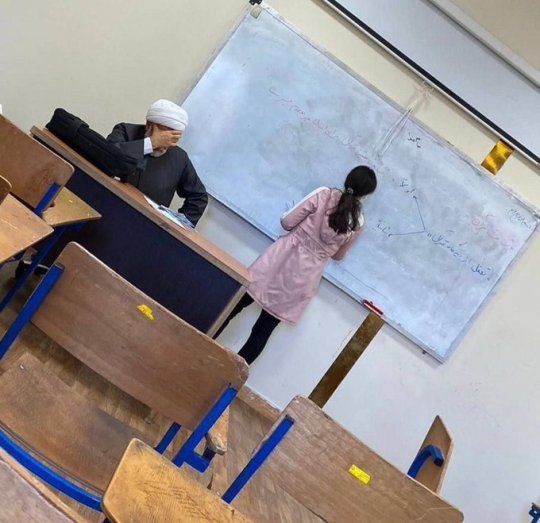







The regime's response to students taking off their hijabs is sending threatening messages to students' phones and increasing the security people. At the entrance of Universities, these security forces check people's clothes and if it's not proper they won't let you in. Some of the students wear the hijab at the entrance and take it off after they're in. They have warned our professors to not let non hijabi students sit in classes too.
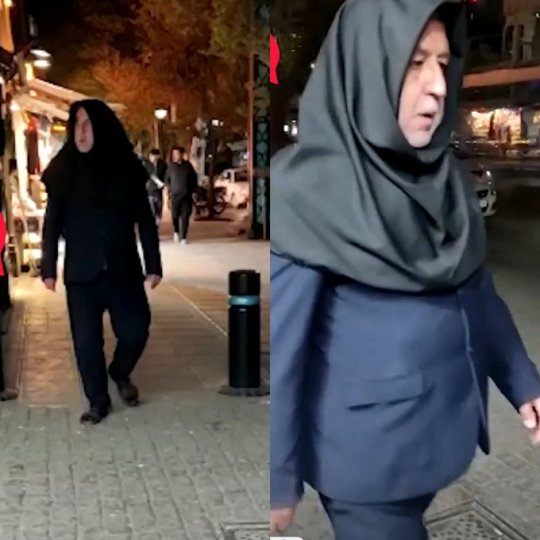
One of my favorite trends in Iran now is when guys wear our hijab. These pictures are from universities. Guys wearing hijab make the security mad. This is a great act of solidarity with women against the obligatory hijab.
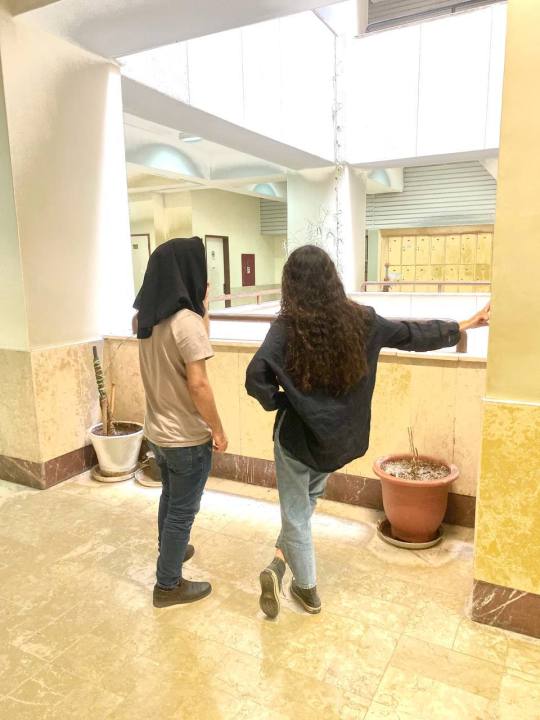
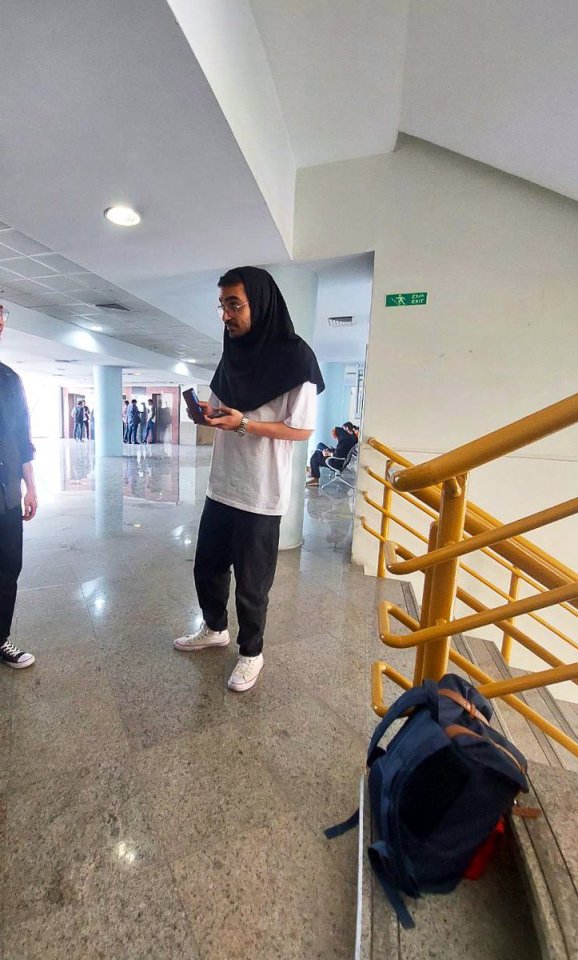
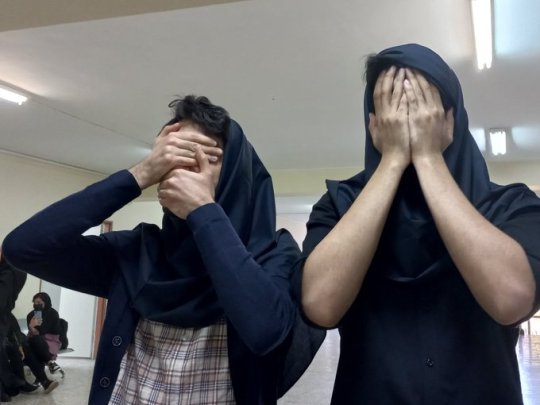
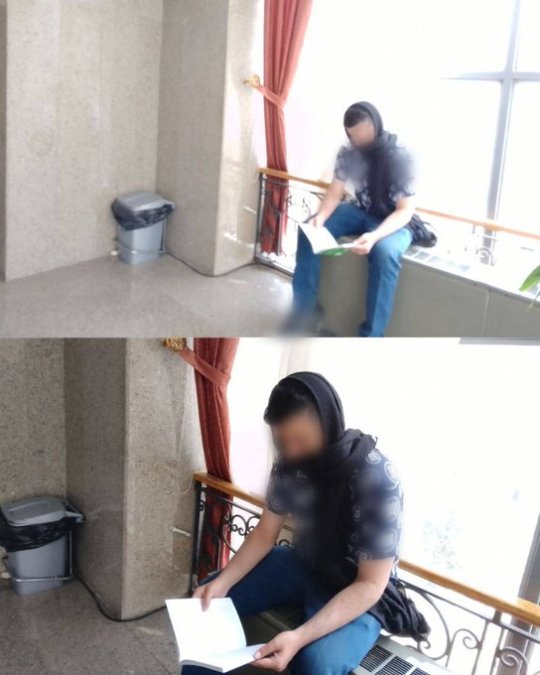




Some men have been doing either this or wearing shorts in public. The former is to ridicule the obligatory dress code and the latter is because wearing shorts in public is forbidden for guys too.
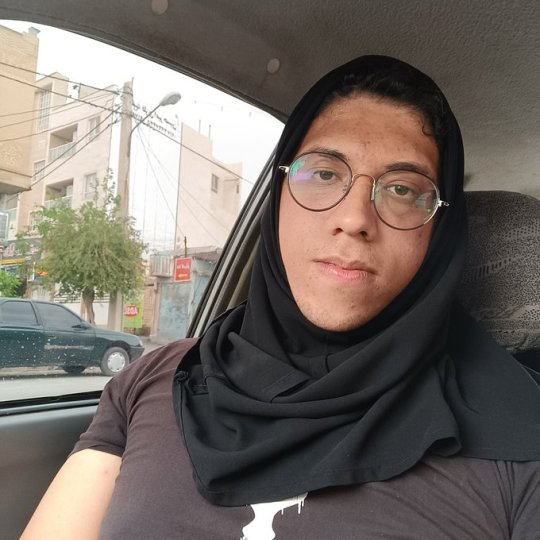
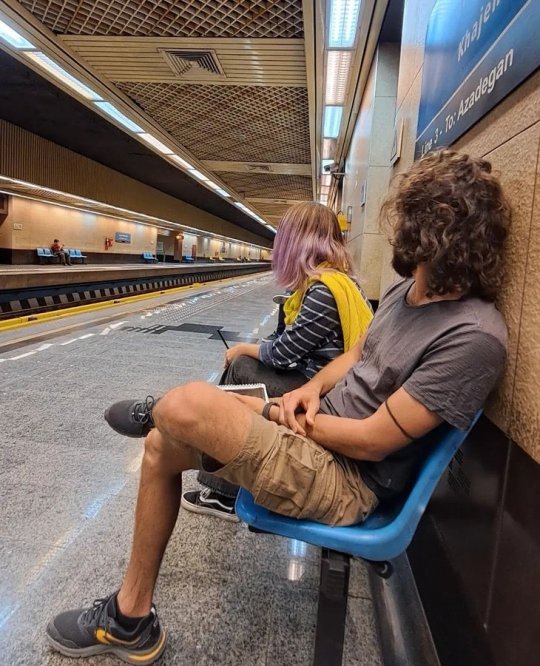
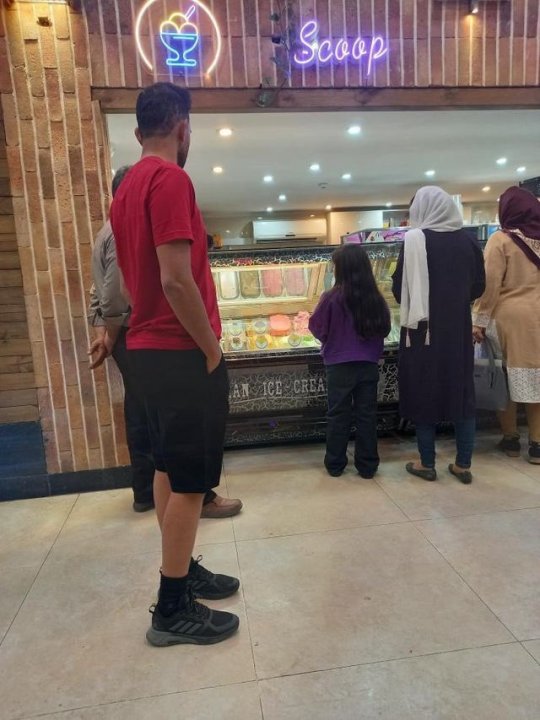




And women not wearing hijab in general. Though hijab is not our only issue, we want a whole new political system, one that is not theocratic or terroristic, hijab is something the regime won't back down from because it's one of their strongest oppressing tools. If they let us win the fight against obligatory hijab, I quote from a regime head, "people keep demanding more changes"!
So to put people against people to enforce the hijab law again, the regime has closed down many businesses (hotels, cafes, malls, bookstores, etc) for welcoming non hijabi female costumers. They have also warned taxi and bus drivers to not let non hijabi women in their vehicles.
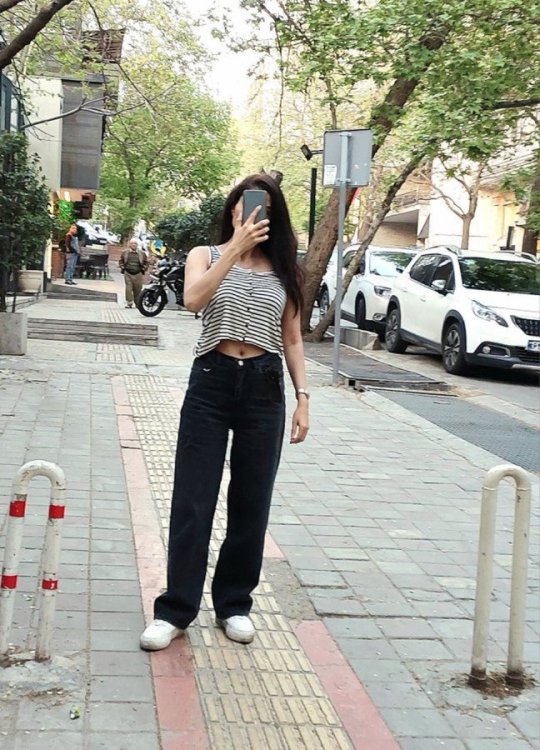
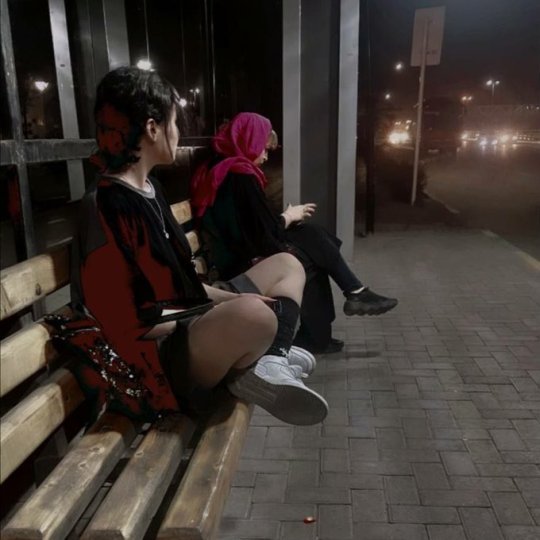
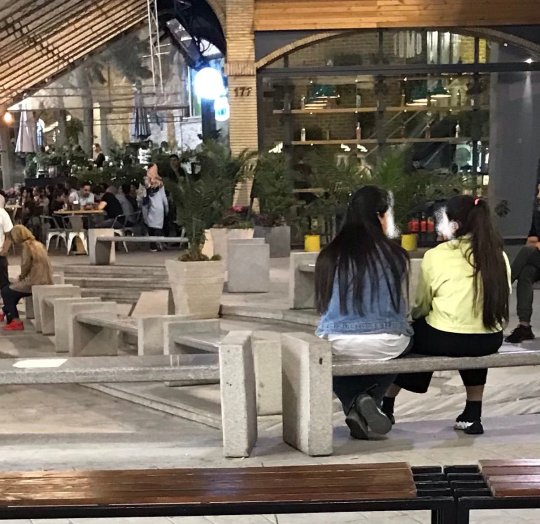
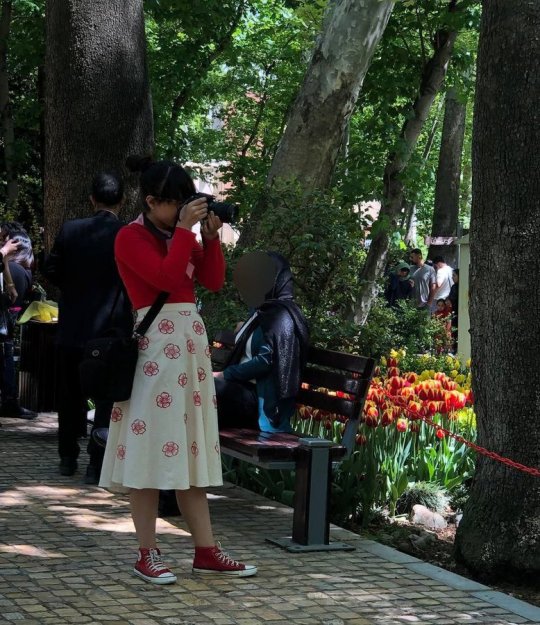
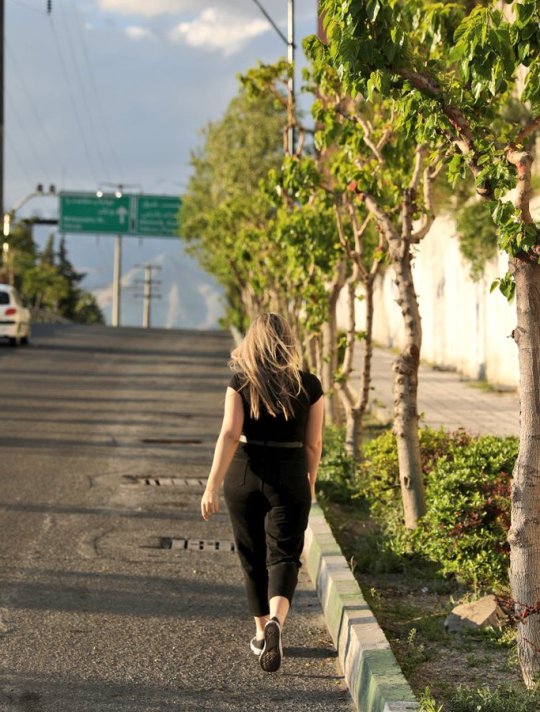
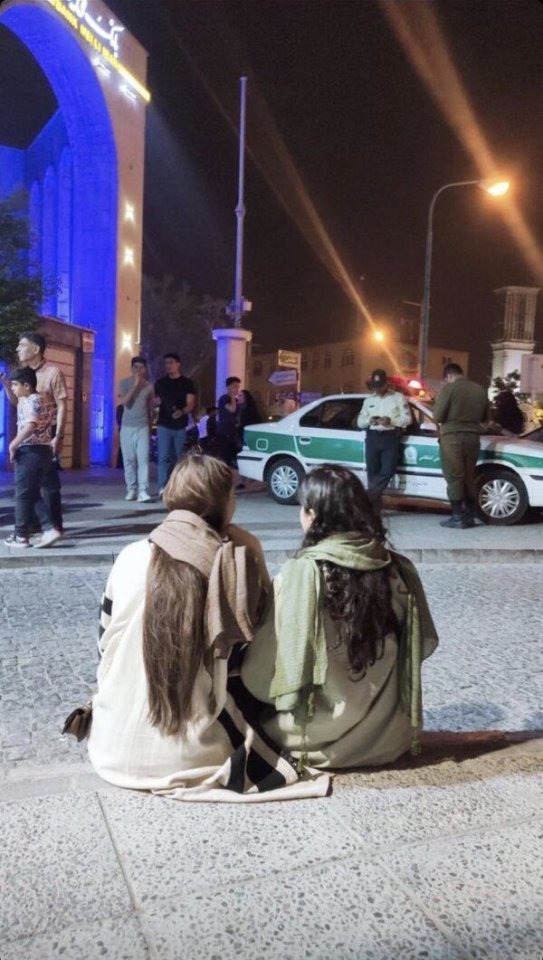
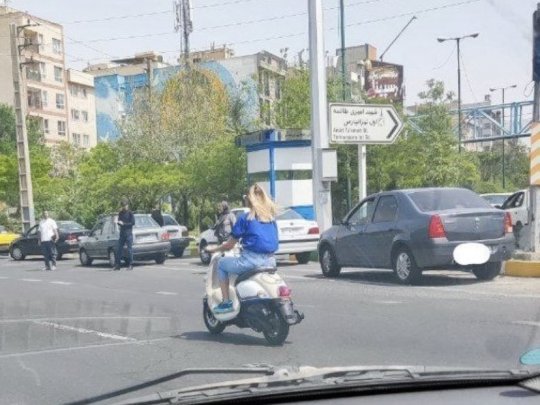
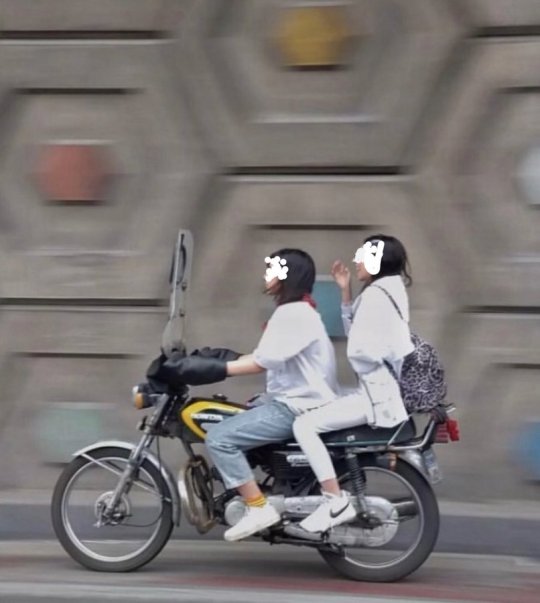









Although not everyone is disobeying the hijab law (some believe in hijab, some don't want to pay the price), the number of women who take the risk and don't wear hijab in Tehran and many other cities is high enough that you feel encouraged to keep doing it.
#iran#iran protests#iran revolution#mahsa amini#jina amini#jin jiyan azadi#women life freedom#politics#human rights#feminism#middle east#women revolution#obligatory hijab#university student#civil disobedience
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

March 8th: International Women's Day
The Palestinian woman: the guardian of the dream and the shield of the revolution
(Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine, 2024)
#pflp#popular front for the liberation of palestine#march 8th#international working women's day#international women's day#free palestine#palestine#feminism#women#guerrilla#communism#revolution#poster#propaganda#posters#2024
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Revolutionary Angela Davis interview in Chicago, 1972
#black art#angela davis#black panthers#black panther party#black tumblr#black history#black women#black hair#black fashion#theafroamericaine#nostalgia#artists on tumblr#classic#revolution#Revolutionary#black culture#history#chicago#america#black community#black girls of tumblr#blog#afro#black women appreciation#usa#black excellence#black experience
223 notes
·
View notes
Text



Some little doodles and inspirational quotes from Camille Desmoulins, Louis Antoine Saint-Just, and Maximilien Robespierre 💖
I've made these 3 cos I'm making some stickers for a comic convention thats very soon, and did the most 'famous' people for starters/who ppl following me might know from my comic :3
But when I have free time I'm definately gonna make some of lesser discussed but equally inspiring revolutionaries~
#It would be awesome to make some of the women and black ppl involved in Frev#I think for ppl not into Frev who are attending cons#sharing such people would be a fun inspiring insight into the history#but I want to do my research first on such people before I make stickers of them#to get their personalities right and find cool quotes~#frev#french revolution#frev art#camille desmoulins#louis antoine saint just#maximilien robespierre#saint just#robespierre
272 notes
·
View notes
Text
Which Underrated Woman from History are You?
Finally got around to making a uquiz featuring six of my favourite women from history! You can either get someone from the French Revolution, Roman Republic (I know, how unexpected!) or from 1700s/early 1800s.
Featuring scientists, writers, politically active icons and a few poets whose lives were intertwined with theirs, as a treat!
Enjoy and thanks everyone for sharing! ✨
#frev#french revolution#ancient rome#roman republic#history#tagamemnon#uquiz#tumblr quiz#which are you?#age of enlightenment#1700s#1800s#romantic era#18th century#19th century#émilie du châtelet#fulvia#clodia#mary shelley#ada lovelace#lord byron#literature#women's history#uquiz link#personality quiz#quiz tag#percy bysshe shelley#lucile desmoulins#camille desmoulins#catullus
290 notes
·
View notes
Text




The Matrix Revolutions, 2003 - dir. The Wachowskis
#monica bellucci#belluccidaily#dailywomen#monicabellucci#vanessa#userklaudia#flawlessbeautyqueens#userrobin#wonderfulwomendaily#breathtakingqueens#persephone#2003#matrix revolutions#the matrix revolutions#women directors#femaledirectedfilms#dailyflicks#usersource#usergif#userstream#userthing#cinematicsource#userladiesofcinema#userladiesblr#m!lfsource#brunettessource#*gifs#*#tvedit#filmedit
377 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Women of the French Revolution (and even the Napoleonic Era) and Their Absence of Activism or Involvement in Films
Warning: I am currently dealing with a significant personal issue that I’ve already discussed in this post: https://www.tumblr.com/nesiacha/765252498913165313/the-scars-of-a-toxic-past-are-starting-to-surface?source=share. I need to refocus on myself, get some rest, and think about what I need to do. I won’t be around on Tumblr or social media for a few days (at most, it could last a week or two, though I don’t really think it will).
But don’t worry about me—I’m not leaving Tumblr anytime soon. I just wanted to let you know so you don’t worry if you don’t see me and have seen this post.
I just wanted to finish this post, which I’d already started three-quarters of the way through.
One aspect that frustrates me in film portrayals (a significant majority, around 95%) is the way women of the Revolution or even the Napoleonic era are depicted. Generally, they are shown as either "too gentle" (if you know what I mean), merely supporting their husbands or partners in a purely romantic way. Just look at Lucile Desmoulins—she is depicted as a devoted lover in most films but passive and with little to say about politics.
Yet there’s so much to discuss regarding women during this revolutionary period. Why don’t we see mention of women's clubs in films? There were over 50 in France between 1789 and 1793. Why not mention Etta Palm d’Alders, one of the founders of the Société Patriotique et de Bienfaisance des Amies de la Vérité, who fought for the right to divorce and for girls' education? Or the cahier from the women of Les Halles, requesting that wine not be taxed in Paris?
Only once have I seen Louise Reine Audu mentioned in a film (the excellent Un peuple et son Roi), a Parisian market woman who played a leading role in the Revolution. She led the "dames des halles" and on October 5, 1789, led a procession from Paris to Versailles in this famous historical event. She was imprisoned in September 1790, amnestied a year later through the intervention of Paris mayor Pétion, and later participated in the storming of the Tuileries on August 10, 1792. Théroigne de Méricourt appears occasionally as a feminist, but her mission is often distorted. She was not a Girondin, as some claim, but a proponent of reconciliation between the Montagnards and the Girondins, believing women had a key role in this process (though she did align with Brissot on the war question). She was a hands-on revolutionary, supporting the founding of societies with Charles Gilbert-Romme and demanding the right to bear arms in her Amazon attire.
Why is there no mention in films of Pauline Léon and Claire Lacombe, two well-known women of the era? Pauline Léon was more than just a fervent supporter of Théophile Leclerc, a prominent ultra-revolutionary of the "Enragés." She was the eldest daughter of chocolatier parents, her father a philosopher whom she described as very brilliant. She was highly active in popular societies. Her mother and a neighbor joined her in protesting the king’s flight and at the Champ-de-Mars protest in July 1791, where she reportedly defended a friend against a National Guard soldier. Along with other women (and 300 signatures, including her mother’s), she petitioned for women’s rights. She participated in the August 10 uprising, attacked Dumouriez in a session of the Société fraternelle des patriotes des deux sexes, demanded the King’s execution, and called for nobles to be banned from the army at the Jacobin Club, in the name of revolutionary women. She joined her husband Leclerc in Aisne where he was stationed (see @anotherhumaninthisworld’s excellent post on Pauline Léon). Claire Lacombe was just as prominent at the time and shared her political views. She was one of those women, like Théroigne de Méricourt, who advocated taking up arms to fight the tyrant. She participated in the storming of the Tuileries in 1792 and received a civic crown, like Louise Reine Audu and Théroigne de Méricourt. She was active at the Jacobin Club before becoming secretary, then president of the Société des Citoyennes Républicaines Révolutionnaires (Society of Revolutionary Republican Women). Contrary to popular belief, there’s no evidence she co-founded this society (confirmed by historian Godineau). Lacombe demanded the trial of Marie Antoinette, stricter measures against suspects, prosecution of Girondins by the Revolutionary Tribunal, and the application of the Constitution. She also advocated for greater social rights, as expressed in the Enragés petition, which would later be adopted by the Exagérés, who were less suspicious of delegated power and saw a role beyond the revolutionary sections.
Olympe de Gouges did not call for women to bear arms; in her Declaration of the Rights of Woman and the Female Citizen, addressed to the Queen after the royal family’s attempted escape, she demanded gender equality. She famously said, "A woman has the right to mount the scaffold; she must equally have the right to mount the rostrum," and denounced the monarchy when Louis XVI's betrayal became undeniable, although she sought clemency for him and remained a royalist. She could be both a patriot and a moderate (in the conservative sense; moderation then didn’t necessarily imply clemency but rather conservative views on certain matters).
Why Are Figures Like Manon Roland Hardly Mentioned in These Films?
In most films, Manon Roland is barely mentioned, or perhaps given a brief appearance, despite being a staunch republican from the start who worked toward the fall of the King and was more than just a supporter of her husband, Roland. She hosted a salon where political ideas were exchanged and was among those who contributed to the monarchy's downfall. Of course, she was one of those courageous women who, while brave, did not advocate for women’s rights. It’s essential to note that just because some women fought in the Revolution or displayed remarkable courage doesn’t mean they necessarily advocated for greater rights for women (even Olympe de Gouges, as I mentioned earlier, had her limits on gender equality, as she did not demand the right for women to bear arms).
Speaking of feminism, films could also spotlight Sophie de Grouchy, the wife and influence behind Condorcet, one of the few deputies (along with Charles Gilbert-Romme, Guyomar, Charlier, and others) who openly supported political and civic rights for women. Without her, many of Condorcet’s posthumous works wouldn’t have seen the light of day; she even encouraged him to write Esquilles and received several pages to publish, which she did. Like many women, she hosted a salon for political discussion, making her a true political thinker.
Then there’s Rosalie Jullien, a highly cultured woman and wife of Marc-Antoine Jullien, whose sons were fervent revolutionaries. She played an essential role during the Revolution, actively involving herself in public affairs, attending National Assembly sessions, staying informed of political debates and intrigues, and even sending her maid Marion to gather information on the streets. Rosalie’s courage is evident in her steadfastness, as she claimed she would "stay at her post" despite the upheaval, loyal to her patriotic and revolutionary ideals. Her letters offer invaluable insights into the Revolution. She often discussed public affairs with prominent revolutionaries like the Robespierre siblings and influential figures like Barère.
Lucile Desmoulins is another figure. She was not just the devoted lover often depicted in films; she was a fervent supporter of the French Revolution. From a young age, her journal reveals her anti-monarchist sentiments (no wonder she and Camille Desmoulins, who shared her ideals, were such a united couple). She favored the King’s execution without delay and wholeheartedly supported Camille in his publication, Le Vieux Cordelier. When Guillaume Brune urged Camille to tone down his criticism of the Year II government, Lucile famously responded, “Let him be, Brune. He must save his country; let him fulfill his mission.” She also corresponded with Fréron on the political situation, proving herself an indispensable ally to Camille. Lucile left a journal, providing historical evidence that counters the infantilization of revolutionary women. Sadly, we lack personal journals from figures like Éléonore Duplay, Sophie Momoro, or Claire Lacombe, which has allowed detractors to argue (incorrectly) that these women were entirely under others' influence.
Additionally, there were women who supported Marat, like his sister Albertine Marat and his "wife"Simone Evrard, without whom he might not have been as effective. They were politically active throughout their lives, regularly attending political clubs and sharing their political views. Simone Evrard, who inspired much admiration, was deeply committed to Marat’s work. Marat had promised her marriage, and she was warmly received by his family. She cared for Marat, hiding him in the cellar to protect him from La Fayette’s soldiers. At age 28, Simone played a vital role in Marat’s life, both as a partner and a moral supporter. At this time, Marat, who was 20 years her senior, faced increasing political isolation; his radical views and staunch opposition to the newly established constitutional monarchy had distanced him from many revolutionaries.
Despite the circumstances, Simone actively supported Marat, managing his publications. With an inheritance from her late half-sister Philiberte, Simone financed Marat’s newspaper in 1792, setting up a press in the Cordeliers cloister to ensure the continued publication of Marat’s revolutionary pamphlets. Although Marat also sought public funds, such as from minister Jean-Marie Roland, it was mainly Simone’s resources that sustained L’Ami du Peuple. Simone and Marat also planned to publish political works, including Chains of Slavery and a collection of Marat’s writings. After Marat’s assassination in July 1793, Simone continued these projects, becoming the guardian of his political legacy. Thanks to her support, Marat maintained his influence, continuing his revolutionary struggle and exposing the “political machination” he opposed.
Simone’s home on Rue des Cordeliers also served as an annex for Marat’s printing press. This setup combined their personal life with professional activities, incorporating security measures to protect Marat. Simone, her sister Catherine, and their doorkeeper, Marie-Barbe Aubain, collaborated in these efforts, overseeing the workspace and its protection.
On July 13, 1793, Jean-Paul Marat was assassinated by Charlotte Corday. Simone Evrard was present and immediately attempted to help Marat and make sure that Charlotte Corday was arrested . She provided precise details about the circumstances of the assassination, contributing significantly to the judicial file that would lead to Corday’s condemnation.
After Marat’s death, Simone was widely recognized as his companion by various revolutionaries and orators who praised her dignity, and she was introduced to the National Convention by Robespierre on August 8, 1793 when she make a speech against Theophile Leclerc,Jacques Roux, Carra, Ducos,Dulaure, Pétion... Together with Albertine Marat (who also left written speeches from this period), Simone took on the work of preserving and publishing Marat’s political writings. Her commitment to this cause led to new arrests after Robespierre's fall, exposing the continued hostility of factions opposed to Marat’s supporters, even after his death.
Moreover, Jean-Paul Marat benefited from the support of several women of the Revolution, and he would not have been as effective without them.
The Duplay sisters were much more politically active than films usually portray. Most films misleadingly present them as mere groupies (considering that their father is often incorrectly shown as a simple “yes-man” in these same, often misogynistic, films, it's no surprise the treatment of women is worse).
Élisabeth Le Bas, accompanied her husband Philippe Le Bas on a mission to Alsace, attended political sessions, and bravely resisted prison guards who urged her to marry Thermidorians, expressing her anger with great resolve. She kept her husband’s name, preserving the revolutionary legacy through her testimonies and memoirs. Similarly, Éléonore Duplay, Robespierre’s possible fiancée, voluntarily confined herself to care for her sister, suffered an arrest warrant, and endured multiple prison transfers. Despite this, they remained politically active, staying close to figures in the Babouvist movement, including Buonarroti, with whom Éléonore appeared especially close, based on references in his letters.
Henriette Le Bas, Philippe Le Bas's sister, also deserves more recognition. She remained loyal to Élisabeth and her family through difficult times, even accompanying Philippe, Saint-Just, and Élisabeth on a mission to Alsace. She was briefly engaged to Saint-Just before the engagement was quickly broken off, later marrying Claude Cattan. Together with Éléonore, she preserved Élisabeth’s belongings after her arrest. Despite her family’s misfortunes—including the detention of her father—Henriette herself was surprisingly not arrested. Could this be another coincidence when it came to the wives and sisters of revolutionaries, or perhaps I missed part of her story?
Charlotte Robespierre, too, merits more focus. She held her own political convictions, sometimes clashing with those of her brothers (perhaps often, considering her political circle was at odds with their stances). She lived independently, never marrying, and even accompanied her brother Augustin on a mission for the Convention. Tragically, she was never able to reconcile with her brothers during their lifetimes. For a long time, I believed that Charlotte’s actions—renouncing her brothers to the Thermidorians after her arrest, trying to leverage contacts to escape her predicament, accepting a pension from Bonaparte, and later a stipend under Louis XVIII—were all a matter of survival, given how difficult life was for a single woman then. I saw no shame in that (and I still don’t). The only aspect I faulted her for was embellishing reality in her memoirs, which contain some disputable claims. But I recently came across a post by @saintejustitude on Charlotte Robespierre, and honestly, it’s one of the best (and most well-informed) portrayals of her.
As for the the hébertists womens , films could cover Sophie Momoro more thoroughly, as she played the role of the Goddess of Reason in her husband’s de-Christianization campaigns, managed his workshop and printing presses in his absence accompanying Momoro on a mission on Vendée. Momoro expressed his wife's political opinion on the situation in a letter. She also drafted an appeal for assistance to the Convention in her husband’s characteristic style.
Marie Françoise Goupil, Hébert’s wife, is likewise only shown as a victim (which, of course, she was—a victim of a sham trial and an unjust execution, like Lucile Desmoulins). However, there was more to her story. Here’s an excerpt from a letter she wrote to her husband’s sister in the summer of 1792 that reveals her strong political convictions:
« You are very worried about the dangers of the fatherland. They are imminent, we cannot hide them: we are betrayed by the court, by the leaders of the armies, by a large part of the members of the assembly; many people despair; but I am far from doing so, the people are the only ones who made the revolution. It alone will support her because it alone is worthy of it. There are still incorruptible members in the assembly, who will not fear to tell it that its salvation is in their hands, then the people, so great, will still be so in their just revenge, the longer they delay in striking the more it learns to know its enemies and their number, the more, according to me, its blows will only strike with certainty and only fall on the guilty, do not be worried about the fate of my worthy husband. He and I would be sorry if the people were enslaved to survive the liberty of their fatherland, I would be inconsolable if the child I am carrying only saw the light of day with the eyes of a slave, then I would prefer to see it perish with me ».
There is also Marie Angélique Lequesne, who played a notable role while married to Ronsin (and would go on to have an important role during the Napoleonic era, which we’ll revisit later). Here’s an excerpt from Memoirs, 1760-1820 by Jean-Balthazar de Bonardi du Ménil (to be approached with caution): “Marie-Angélique Lequesne was caught up in the measures taken against the Hébertists and imprisoned on the 1st of Germinal at the Maison d'Arrêt des Anglaises, frequently engaging with ultra-revolutionary circles both before and after Ronsin’s death, even dressing as an Amazon to congratulate the Directory on a victory.” According to Généanet (to be taken with even more caution), she may have served as a canteen worker during the campaign of 1792.
On the Babouvist side, we can mention Marie Anne Babeuf, one of Gracchus Babeuf’s closest collaborators. Marie Anne was among her husband's staunchest political supporters. She printed his newspaper for a long time, and her activism led to her two-day arrest in February 1795. When her husband was arrested while she was pregnant, she made every effort possible to secure his release and never gave up on him. She walked from Paris to Vendôme to attend his trial, witnessing the proceeding that would sentence him to death. A few months after Gracchus Babeuf’s execution, she gave birth to their last son, Caius. Félix Lepeletier became a protector of the family (and apparently, Turreau also helped, supposedly adopting Camille Babeuf—one of his very few positive acts). Marie Anne supported her children through various small jobs, including as a market vendor, while never giving up her activism and remaining as combative as ever. (There’s more to her story during the Napoleonic era as well).
We must not forget the role of active women in the insurrections of Year III, against the Assembly, which had taken a more conservative turn by then. Here’s historian Mathilde Larrère’s description of their actions: “In April and May 1795, it was these women who took to the streets, beating drums across the city, mocking law enforcement, entering shops, cafes, and homes to call for revolt. In retaliation, the Assembly decreed that women were no longer allowed to attend Assembly sessions and expelled the knitters by force. Days later, a decree banned them from attending any assemblies and from gathering in groups of more than five in the streets.”
There were also women who fought as soldiers during the French Revolution, such as Marie-Thérèse Figueur, known as “Madame Sans-Gêne.” The Fernig sisters, aged 22 and 17, threw themselves into battle against Austrian soldiers, earning a reputation for their combat prowess and later becoming aides-de-camp to Dumouriez. Other fighting women included the gunners Pélagie Dulière and Catherine Pochetat.
In the overseas departments, there was Flore Bois Gaillard, a former slave who became a leader of the “Brigands” revolt on the island of Saint Lucia during the French Revolution. This group, composed of former slaves, French revolutionaries, soldiers, and English deserters, was determined to fight against English regiments using guerrilla tactics. The group won a notable victory, the Battle of Rabot in 1795, with the assistance of Governor Victor Hugues and, according to some accounts, with support from Louis Delgrès and Pelage.
On the island of Saint-Domingue, which would later become Haiti, Cécile Fatiman became one of the notable figures at the start of the Haitian Revolution, especially during the Bois-Caiman revolt on August 14, 1791.
In short, the list of influential women is long. We could also talk about figures like Félicité Brissot, Sylvie Audouin (from the Hébertist side), Marguerite David (from the Enragés side), and more. Figures like Theresia Cabarrus, who wielded influence during the Directory (especially when Tallien was still in power), or the activities of Germaine de Staël (since it’s essential to mention all influential women of the Revolution, regardless of political alignment) are also noteworthy.
Napoleonic Era
Films could have focused more on women during this era. Instead, we always see the Bonaparte sisters (with Caroline cast as an exaggerated villain, almost like a cartoon character), or Hortense Beauharnais, who’s shown solely as a victim of Louis Bonaparte and portrayed as naïve. There is so much more to say about this time, even if it was more oppressive for women.
Germaine de Staël is barely mentioned, which is unfortunate, and Marie Anne Babeuf is even more overlooked, despite her being questioned by the Napoleonic police in 1801 and raided in 1808. She also suffered the loss of two more children: Camille Babeuf, who died by suicide in 1814, and Caius, reportedly killed by a stray bullet during the 1814 invasion of Vendôme. No mention is made of Simone Evrard and Albertine Marat, who were arrested and interrogated in 1801.
An important but lesser-known event in popular culture was the deportation and imprisonment of the Jacobins, as highlighted by Lenôtre. Here’s an excerpt: “This petition reached Paris in autumn 1804 and was filed away in the ministry's records. It didn’t reach the public, who had other amusements besides the old stories of the Nivôse deportees. It was, after all, the time when the Republic, now an Empire, was preparing to receive the Pope from Rome to crown the triumphant Caesar. Yet there were people in Paris who thought constantly about the Mahé exiles—their wives, most left without support, living in extreme poverty; mothers were the hardest hit. Even if one doesn’t sympathize with the exiles themselves, one can feel pity for these unfortunate women... They implored people in their neighborhoods and local suppliers to testify on behalf of their husbands, who were wise, upstanding, good fathers, and good spouses. In most cases, these requests came too late... After an agonizing wait, the only response they received was, ‘Nothing to be done; he is gone.’” (Les Derniers Terroristes by Gérard Lenôtre). Many women were mobilized to help the Jacobins. One police report references a woman named Madame Dufour, “wife of the deportee Dufour, residing on Rue Papillon, known for her bold statements; she’s a veritable fury, constantly visiting friends and associates, loudly proclaiming the Jacobins’ imminent success. This woman once played a role in the Babeuf conspiracy; most of their meetings were held at her home…” (Unfortunately for her, her husband had already passed away.)
On the Napoleonic “allies” side, Marie Angélique, the widow of Ronsin who later married Turreau, should be more highlighted. Turreau treated her so poorly that it even outraged Washington’s political class. She was described as intelligent, modest, generous, and curious, and according to future First Lady Dolley Madison, she charmed Washington’s political circles. She played an essential role in Dolley Madison’s political formation, contributing to her reputation as an active, politically involved First Lady. Marie Angélique eventually divorced Turreau, though he refused to fund her return to France; American friends apparently helped her.
Films could also portray Marie-Jacqueline Sophie Dupont, wife of Lazare Carnot, a devoted and loving partner who even composed music for his poems. Additionally, her ties with Joséphine de Beauharnais could be explored. They were close friends, which is evident in a heartbreaking letter Lazare Carnot wrote to Joséphine on February 6, 1813, to inform her of Sophie’s death: “Until her last moment, she held onto the gratitude Your Majesty had honored her with; in her memory, I must remind Your Majesty of the care and kindness that characterize you and are so dear to every sensitive soul.”
In films, however, when Joséphine de Beauharnais’s circle is shown, Theresia Cabarrus (who appears much more in Joséphine ou la comédie des ambitions) and the Countess of Rémusat are mentioned, but Sophie Carnot is omitted, which is a pity. Sophie Carnot knew how to uphold social etiquette well, making her an ideal figure to be integrated into such stories (after all, she was the daughter of a former royal secretary).
Among women soldiers, we had Marie-Thérèse Figueur as well as figures like Maria Schellink, who also deserves greater representation. Speaking of fighters, films could further explore the stories of women who took up arms against the illegal reinstatement of slavery. In Saint-Domingue, now Haiti, many women gave their lives, including Sanité Bélair, lieutenant of Toussaint Louverture, considered the soul of the conspiracy along with her husband, Charles Bélair (Toussaint’s nephew) and a fighter against Leclerc. Captured, sentenced to death, and executed with her husband, she showed great courage at her execution. Thomas Madiou's Histoire d’Haiti describes the final moments of the Bélair couple: “When Charles Bélair was placed in front of the squad to be shot, he calmly listened to his wife exhorting him to die bravely... (...)Sanité refused to have her eyes covered and resisted the executioner’s efforts to make her bend down. The officer in charge of the squad had to order her to be shot standing.”
Dessalines, known for leading Haiti to victory against Bonaparte, had at least three influential women in his life. He had as his mentor, role modele and fighting instructor the former slave Victoria Montou, known as Aunt Toya, whom he considered a second mother. They met while they were working as slaves. They met while both were enslaved. The second was his future wife, Marie Claire Bonheur, a sort of war nurse, as described in this post, who proved instrumental in the siege of Jacmel by persuading Dessalines to open the roads so that aid, like food and medicine, could reach the city. When independence was declared, Dessalines became emperor, and Marie Claire Bonheur, empress. When Jean-Jacques Dessalines ordered the elimination of white inhabitants in Haiti, Marie Claire Bonheur opposed him, some say even kneeling before him to save the French. Alongside others, she saved those later called the “orphans of Cap,” two girls named Hortense and Augustine Javier.
Dessalines had a legitimized illegitimate daughter, Catherine Flon, who, according to legend, sewed the country’s flag on May 18, 1803. Thus, three essential women in his life contributed greatly to his cause.
In Guadeloupe, Rosalie, also known as Solitude, fought while pregnant against the re-establishment of slavery and sacrificed her life for it, as she was hanged after giving birth. Marthe Rose Toto also rose up and was hanged a few months after Louis Delgrès’s death (if they were truly a couple, it would have added a tragic touch to their story, like that of Camille and Lucile Desmoulins, which I have discussed here).
To conclude, my aim in this post is not to elevate these revolutionary, fighting, or Napoleonic-allied women above their male counterparts but simply to give them equal recognition, which, sadly, is still far from the case (though, fortunately, this is not true here on Tumblr).
I want to thank @aedesluminis for providing such valuable information about Sophie Carnot—without her, I wouldn't have known any of this. And I also want to thank all of you, as your various posts have been really helpful in guiding my research, especially @anotherhumaninthisworld, @frevandrest, @sieclesetcieux, @saintjustitude, @enlitment ,@pleasecallmealsip ,@usergreenpixel , @orpheusmori ,@lamarseillasie etc. I apologize if I forgot anyone—I’m sure I have, and I'm sorry; I'm a bit exhausted. ^^

























#frev#french revolution#napoleon#napoleonic era#women in history#haitian revolution#slavery#guadeloupe#frustration
117 notes
·
View notes
Text
Women's Suffrage Movement

The movement for women's suffrage took many decades to obtain voting rights. Women fought for their rights via smart political strategy. Dynamic leadership attracted several generations of women – mothers, daughters, and grandmothers formed national organizations and made alliances that brought women into the political sphere. The fight intensified during World War I due to women's work outside the home to help the war effort. Women now saw themselves as fully deserving of the same rights as men.

A trio of outfits at the Daughters of the American Revolution Museum shows the evolution from the last gasp of Edwardian bulk to the short, simple dress of the Twenties. Left, a two-piece dress of about 1907 (Daughters of the American Revolution Museum). Center, a houndstooth suit of about 1914 (loan courtesy Shippensburg University Fashion Archives and Museum). Right, black and white day dress, 1925 (Daughters of the American Revolution Museum).




Exhibition vignette with the “Bear the Banner Proudly They Have Borne Before” banner, circa 1913-1920. National Woman’s Party. Belmont-Paul Women’s Equality National Monument, Washington, DC.
Purple, white, and gold were among the colors representing the movement. White dresses were worn by women as a representation of purity of thought and high-mindedness. Purple represented the vote and loyalty, constancy, and steadfastness. Gold stood for the torch that guides our way.



Ethel Wright (1866–1939) Christabel Pankhurst (British suffragette) • National Portrait Gallery, London
#fashion history#women's history#suffrage movement#women's voting rights#white dresses of the suffrage movement#colors of women's suffrage#daughters of the american revolution#late 19th – early 20th century women's fashion#the resplendent outfit art & fashion blog#ethel wright#woman artist#christabel pankhurst#suffrage fashion#historical photos
103 notes
·
View notes
Text
Today marks one year anniversary of 2022 Iranian uprising against the oppressive Islamic Republic regime. An uprising that started with the brutal murder of a young kurd woman, Mahsa Jina Amini, for "inappropriate hijab".
For the past couple of weeks, the regime has prepared their forces to beat down any new movement immediately. The streets of Tehran and many other cities are lined with anti riot forces and police cars. In Saqez, the home city of Amini family, they've stationed the army around the city to massacre people in case they try to start another wave of protest. Mahsa's father has been arrested alongside some family members of other last year uprising martyrs.
There has been small protesting gatherings in Iran in the last two days, there has already been some arrests and violent crackdowns on protesters. I hear people chanting from my neighborhood homes. The government would commit as many bloodbaths as it takes to secure their position, but you can't beat people into obedience when they hate you from the bottom of their hearts.
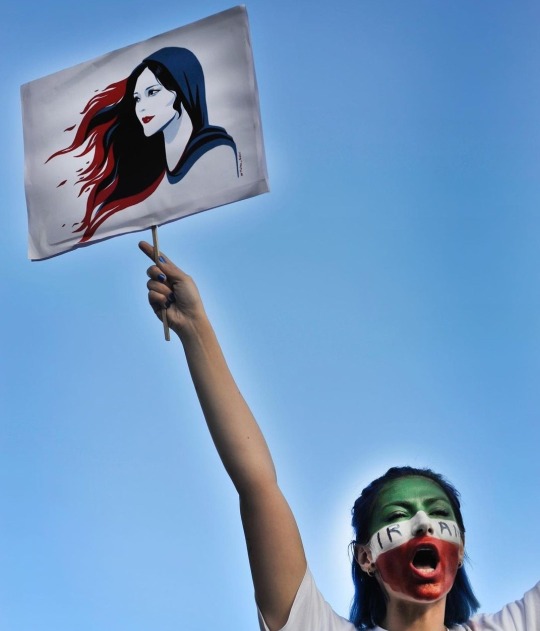

Woman life freedom
#iran#mahsa amini#iran protests#human rights#iran revolution#women's rights#middle east#politics#woman life freedom
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Historians having takes on frev women that make me go 😐 compilation
Sexually frustrated in her marriage to a pompous civil servant much older than herself, [Madame Roland] may have found Danton’s celebrated masculinity rather uncomfortable. Danton (1978) by Norman Hampson, page 77.
The Robespierres sent their sister to Arras because that was their hometown, the family home, where they had relatives, uncles, aunts and friends, like Buissart who they didn’t cease to remain in correspondence with, even in the middle of the Terror. There, among them, Charlotte would not be alone; she would find advice, rest, the peace necessary to heal her nervousness and animosity. Away from Mme Ricard, who she hated, away from Mme Duplay, who she detested, she would enjoy auspicious calmness. It is Le Bon that the Robespierres will charge with escorting their sister to this neccessary and soothing exile. […] If there is a damning piece in Charlotte Robespierre's case, it is this one (her interrogation, held July 31 1794). She seems to be caught in the act of accusing this Maximilien whom she rehabilitates in her Memoirs. She is therefore indeed a hypocrite, unworthy of the great name she bears, and which she dishonors the very day after the holocaust of 10 Thermidor. Charlotte Robespierre et Guffroy (1910) in Annales Révolutionnaires, volume 3 (1910) page 322, and Charlotte Robespierre et ses mémoires (1909) page 93-94, both by Hector Fleishmann.
Elisabeth, as she was popularly called, was barely past her twelfth birthday, younger even by three years than Barere’s own mother when she was given in marriage. On the following day the guests assembled again in the little church of Saint-Martin at midnight to attend the wedding ceremony of the handsome charmer and the bewildered child. Dressed in white, clasping in her arms a yellow, satin-clad doll that Bertrand had given her — so runs the tradition — she marched timidly to the altar, looking more like a maiden making her first communion than a woman celebrating a binding sacrament. Perhaps the doll, if doll there was, filled her eye, but certainly she could not fail to note how handsome her husband was. Bertrand Barere; a reluctant terrorist (1962) by Leo Gershoy, page 32.
The young nun who bore the name of Hébert did not hide her fate. She did not wish to prolong a life stifled from her childhood in the cloister, branded in the world by the name she bore, fighting between horror and love for the memory of her husband, unhappy everywhere. Histoire des Girondins (1848) by Alphonse de Lamartine, volume 8, page 60.
Lucile in prison showed more calmness than Camille. Before the tribunal, she seemed to possess neither fear nor hope, she denied having taken an active role in the prison conspiracy. What did it matter to her the answer they were trying to extract from her? They said they wanted her guilty? Very well! She would be condemned and join Camille. This was what she said again when she was told that she would suffer the same fate as her husband: ”Oh, what joy, in a few hours I’m going to see Camille again!” Camille et Lucile Desmoulins: un couple dans la tourmente (1986) by Jean Paul Bertaud, page 293.
What did it matter to Lucile whether she was accused or defended? She had no longer any pretext for living in this world. She was one of those heroines of conjugal love who are more wife than mother. Besides, Horace lived, and Camille was dead. It was of the absent only that she thought. As for the child, would not Madame Duplessis act a mother's part to him? The grandmother would watch over the orphan. If Lucile had lived, she could have done nothing but weep over the cradle, thinking of Camille. Camille Desmoulins and his wife; passages from the history of the Dantonists founded upon new and hitherto unpublished documents (1876) by Jules Claretie.
Having been widowed at the age of 23 [sic] years, Élisabeth Duplay remarried a few years later to the adjutant general Le Bas, brother of her first husband, and kept the name which was her glory. She lived with dignity, and all those who have known her, still beautiful under her crown of white hair, have testified to the greatness of her sentiments and austerity of her character. She died at an old age, always loyal to the memory of the great dead she had loved and whose memory she, all the way to her final day, didn’t cease to honor and cherish. As for the lady of Thermidor, Thérézia Cabarrus, ex-marquise of Fontenay, citoyenne Tallien, then princess of Chimay, one knows the story of her three marriages, without counting the interludes. She had, as one knows, three husbands living at the same time. Now compare these two existances, these two women, and tell me which one merits more the respect and the sympathy of good men. Histoire de Robespierre et du coup d’état du 9 thermidor (1865) by Louis Ernest Hamel, volume 3, page 402.
Fel free to comment which one was your favorite! 😀
#frev#french revolution#frev compilation#hampson: if women were uncomfortable around danton it’s because they were sexually frustrated!#fleishmann: two men in their 30s can ultimately decide what’s best for their sister who’s also in her 30s#also it’s totally unreasonable for charlotte to disown her brothers after their death when her life was possibly in danger#(and even though they pretty much disowned her while they were still alive)#lamartine claretie bertaud: françoise and lucile wanted to die since there was no longer any point to their lives after the husbands died#hamel: a good way of finding out which side was bad and which side was good is to look over how slutty the women on each side were#wow are you seriously surprised the view of women held by 19th century authors isn’t exactly top modern?#…no comment#claretie should technically get a pass since he thought the journal of sanson was an authentic source#But it was so spectacular i couldn’t contain myself#also a shame i couldn’t remember where i read the interpretation that the reason simond évrard was wary of charlotte corday#was bc she might seduce marat when alone with him
90 notes
·
View notes
Text




#international women's day#international working women's day#posters#propaganda#feminism#women#women's rights#communism#pflp#palestine#eritrea#ireland#germany#revolution#eplf#ira#guerrilla#march 8th#march 8#8 de marzo
872 notes
·
View notes
Text

#Anuradha Ghandy#women's liberation#the philippines#flip#cpp#npa#revolution#revolutionary#marxism leninism maoism#marxism#maoism#communism#communist#maoist#socialism#MLM
562 notes
·
View notes
Text

This October 5, 2024, Cookie wishes you an eventful 235th anniversary of the Women’s March on Versailles!
#cats#cookie#cookie wishes you#cat#cute cats#2024#date#history#animals#this day in history#french revolution#french history#women#women in history
84 notes
·
View notes
Text
Wu Shuqing and the revolutionary women's troops

Revolutionary women fighting at Nanjing
In 1911, revolutionaries in southern China rose up against the Manchu-led Qing Dynasty. Their successful uprising brought an end to the imperial system and ushered in the early republican era. Moved by both patriotism and feminist ideals, women joined the movement.
Wu Shuqing’s women’s troop
Wu Shuqing, a 19-year-old student from Hanyang, was one of these women. Alongside two others, she wrote to revolutionary leader Li Yuanhong, asking for permission to fight. He initially refused, arguing that integrating women into an all-male army would be too difficult.
But Wu Shuqing didn’t back down. She responded by asserting that there was no difference between men and women when it came to fighting a revolution:
“Were they to hear that the nation was conscripting troops, farmers would lay down their hoes and laborers would abandon their tools. In high spirit they would go off and become soldiers. Even teachers and students in school would all have to become troops. The people are the starting point for society, and society is the point at which the state begins. The people are thus of major importance in terms of victory and defeat of the state. If we do not now come to the aid of the great Han people and wipe out the Manchu bastards, we will assuredly earn the slander of foreigners. In the north sits powerful Russia and majestic Great Britain. Our country faces great dangers on that front. I seek no instant glory. I merely want to join the troops in fighting northward, giving my life in pursuit of the enemy, killing the Manchus. Only then will our Han race be avenged.”
Wu Shuqing’s request was granted, and a women’s troop was formed.
The women’s troop at the front
The exact number of women who joined is unclear, with reports suggesting several hundred. They underwent military training before being sent to the front lines.
Wu Shuqing led them into combat. She participated in a campaign against the Qing at Hankou. During the battle for Nanjing, she and her troops devised a plan to occupy the fort at Shizishan, opening a path for the revolutionary army.
Many women’s forces and organizations were formed in quick succession, though not all of them saw battle.
The sisters Yin Weijun and Yin Ruizhi became famous for their skill in bomb-making and explosives. They earned respect during the battles against the Qing for their daring bombing raids.
Though Yin Ruizhi was wounded, her sister went on to create another unit, the Zhejiang Women’s Nationalist Army, leading them into battle. Over 30 women from this unit fought to liberate Nanjing. They attacked three forts, occupied Yuhatai, scaled ladders over the city walls, and entered Nanjing on December 2. Eyewitnesses praised their bravery and combat effectiveness. However, the troop was later disbanded as the commander-in-chief did not believe women could handle a long-term expedition.

The Yin sisters in military attire.
A third women’s troop also participated in the battle for Nanjing, providing first-aid and logistical support.
A fourth women’s unit, the Guandong Women’s Northern Expedition Bombing Team, was led by Xu Mulan. A hundred female soldiers fought at Xu Zhou.
Though women made up only a small fraction of the revolutionary forces, they played a vital role in the overall movement. For some, their military involvement became a way to express their political ideals and ensure the possibility of an egalitarian society in the future republic. Some of these women also became outspoken advocates for women’s suffrage.
Aftermath
Most women’s armies were discharged in 1912 after a compromise was reached between the revolutionaries and the northern forces. Many female soldiers were left frustrated, feeling that their contributions were undervalued, especially as all positions in the provisional government were given to men.
Wu Shuqing’s whereabouts after the revolution remain unknown.
Here is the link to my Ko-Fi. Your support would be much appreciated!
Further reading:
Edwards Louise, Gender, Politics, and Democracy: Women's Suffrage in China
Ono Kazuko, Chinese Women in a Century of Revolution, 1850-1950
Li Xiaolin, Women in the Chinese Military
#history#women in history#wu shuqing#women's history#china#chineses revolution#chinese history#asian history#warrior women#female soldiers#20th century#Yin Weijun#Yin Ruizhi#Xu Mulan#historyblr
82 notes
·
View notes
Text
If you believe at all in astrology or psychic abilities, please do not ignore this. Pluto is moving into Aquarius on the 19th of this month, aka the planet associated with innovation, equality, and REVOLUTION, after the shitshow that was the American presidential election. This is the first time in over 200 years this has happened, (the American Revolution started 248 years ago, which is also the last time Pluto was in Aquarius!!!) Aquarius is the sign driving us to consider collective ideals, humanitarian improvement, utopia vs dystopia in our society, I mean, helloooo!!! Pluto's strongest potential is in EMPOWERMENT. I just felt very drawn to look into this and share with ya'll. I know not everyone believes in astrology or witchcraft, but the spiritually tuned in knew when trump was elected, I myself had a dream that he was elected and woke up the next day and he had. Of course this is majorly scary, but many psychics have been feeling and receiving peaceful signs that it will be okay or that now is the time to be bold. This is kind of the biggest astrological deal of our era. For those who practice please do what you can to protect yourselves, spread news of this and manifest all good and positive things for our collective future. Pluto will remain in Aquarius until 2043, almost 20 years, so get ready for some big changes. Love ya'll, stay safe and don't give up <3
#pluto in aquarius#astrology#pluto#aquarius#2024 presidential election#election 2024#pagan witch#witchcraft#witchblr#astrological#astrological events#astrological transits#us politics#revolution#fuck trump#trans rights#queer rights#gay rights#women's rights#psychic#psychic abilities
64 notes
·
View notes
Note
you say machete has to be closeted then why's he always wearing them little heels
Maybe he thinks he's a tiny bit nicer looking in them.
#no in fact he's just a little ahead of the curve let me try to explain#again I'm not a historian I'm just sharing what I've read I might be misremembering stuff so don't quote me on this#high heels became extremely fashionable in the early 1600's probably just a few decades after Machete's time#and they were originally worn by men#because they were inspired by Persian riding boots#if your shoes had heels you'd have easier time keeping your feet in the stirrups (think of cowboy boots)#Europeans saw them thought they looked snazzy and they became wildly popular in noble circles fairly quickly#for some hundred years or so high heels were the epitome of class wealth power and status and they were essentially genderless#remember that concepts of masculinity and femininity are fluid and change over time#things that were seen as manly a few centuries ago may seem downright effeminate to a modern viewer#it's all matter of perspective neither is objectively more correct than the other#they started to separate into men's heels and women's heels around mid 1700's iirc but the changes weren't massive even then#and only truly went out of vogue when the French Revolution hit in 1789#and people all across the continent were suddenly put off by everything that reminded them#of the frivolousness and extravagance of royalty and aristicracy#so in his canon timeline I don't think people are looking at him and going “hmmm that's pretty gay”#because heels hadn't become gendered yet#maybe he likes how they accentuate his already tiny paws and make his legs look even longer than they are#he's interested in fashion or at least likes to dress nicely in high quality garments#he tries very hard to look his best despite never really feeling comfortable in his skin#he was a real shrimp as a kid and even though he eventually grew up to be a beanpole he might still find the extra height appealing#no one's going to look down on him ever again#I admit the way I draw them is a lot more modern than the true historical style at the time but not outrageously so#artistic freedom and all that in the end I'm not aiming for 100% accuracy#modern au Machete has no excuses though he's just a little bit fruity#if the guy feels empowered by wearing little clip cloppers let him#answered#anonymous#Machete
391 notes
·
View notes